Uterine Fibroids In Nagpur
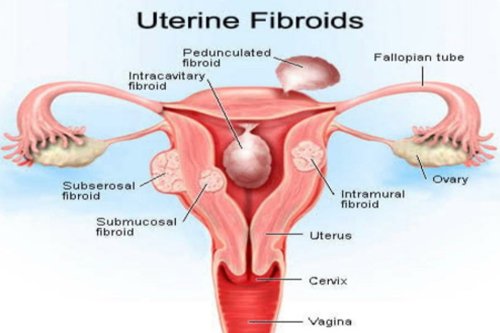
Uterine Fibroids Symptoms
Menstrual Changes:
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Menorrhagia): Excessive menstrual bleeding that may lead to prolonged periods or the need to change tampons or pads frequently.
- Menstrual Periods Lasting Longer than a Week: Extended duration of menstrual bleeding.
Pelvic Pain or Pressure:
- Pelvic Pain: A dull or aching pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis.
- Pelvic Pressure: A feeling of fullness or pressure in the lower abdomen.
Pelvic Discomfort or Backache: Discomfort or pain in the pelvis or lower back.
Frequent Urination or Difficulty Emptying the Bladder: Fibroids pressing on the bladder may lead to an increased frequency of urination or difficulty fully emptying the bladder.
Pain During Sexual Intercourse: Pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse, particularly if fibroids affect the uterine wall or cervix.
Enlarged Abdomen or Uterus: Large fibroids or a cluster of fibroids can cause the uterus to enlarge, leading to an enlarged abdomen.
Constipation or Bloating: Fibroids pressing on the rectum may cause constipation or a feeling of bloating.
Complications During Pregnancy and Labor: Fibroids can sometimes lead to complications during pregnancy, such as a higher risk of cesarean section (C-section) or breech birth.
Treatment of Uterine Fibroids
1. Medications:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
- Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, can help manage pain and reduce menstrual cramps.
- Hormonal Medications:
- Birth control pills, hormonal patches, or hormonal intrauterine devices (IUDs) can help regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists may be used to induce a temporary menopausal state, shrinking fibroids and reducing symptoms.
2. Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE):
- A minimally invasive procedure in which the blood supply to the fibroids is blocked, leading to their shrinkage.
- UFE is an alternative to surgical options for women who want to preserve their uterus.
3. Myomectomy:
- Surgical removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus.
- Myomectomy may be considered for women who wish to retain fertility or avoid a hysterectomy.
4. Hysterectomy:
- Surgical removal of the uterus.
- Hysterectomy is a definitive treatment for fibroids and is considered when other treatments are not effective or when fertility preservation is not a concern.
5. Endometrial Ablation:
- A procedure that removes or destroys the lining of the uterus, often used to treat heavy menstrual bleeding associated with fibroids.
6. Focused Ultrasound Surgery (FUS):
- A noninvasive procedure that uses focused ultrasound waves to heat and destroy fibroid tissue.
7. Laparoscopic or Robotic Surgery:
- Minimally invasive surgical approaches to remove or treat fibroids.
- These procedures may be considered for specific cases, such as subserosal fibroids or those causing significant symptoms.
8. Complementary Therapies:
- Acupuncture or Yoga:
- Some women find relief from symptoms through complementary therapies, although research on their effectiveness is limited.
